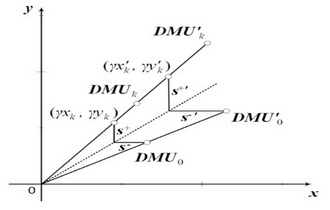
Data Envelopment Analysis(DEA) simultaneously provides both the efficiency scores and targets of inefficient DMUs, and these two pieces of information are usually inseparable. If an inefficient DMU is far from its target, it will be impossible to reach it in a single move, the more reasonable alternative being to make stepwise gradual improvements in getting to the target.
This paper, under CRS assumption, proposed a method that help us to determine benchmarking paths which consider the improvement steps as the learning of the production functions, not the learning of inputs and outputs. First, the paper proposed a model to find the closest target among efficient DMUs. Next, to determine stepwise improvements for inefficient DMUs, stratification was carried out. Finally, the paper used Dijkstra's algorithm to find the shortest paths to the ultimate targets in terms of the whole path. For this, the paper defined a distance concept that reflects the degree of proximity between production functions of two DMUs, composed the directed weighted graph, and suggested the algorithm to find the shortest paths(Fig.1)
The method proposed in this study can be applied in various forms. For example, in case of the number of DMUs is small, the historical data can be used together to set intermediate and ultimate targets for path determination. In addition, for some DMUs which have the ability to leap to multiple levels at once, we can newly construct weighted direction graphs and find the shortest paths.
The results were published in "Expert Systems With Applications" under the title of "Stepwise benchmarking based on production function: Selecting path towards closest target" (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120308).